1. Hello World
Taken from prosperocoder.com
Well, we’re going to write a basic Kivy app that will display the Hello World text. In Kivy, like in many other GUI libraries and frameworks, static text is usually displayed in a label. In Kivy we call simple GUI elements like labels, buttons, sliders, check boxes, etc. widgets, although widgets don’t have to be simple at all and you can create your own widgets, which we are going to do later.
Anyway, our program is going to display the text Hello World in a label. Before we write the code, let’s create a folder where we will save it. Then open the folder in your editor or IDE. Here’s how to do it in Visual Studio Code:
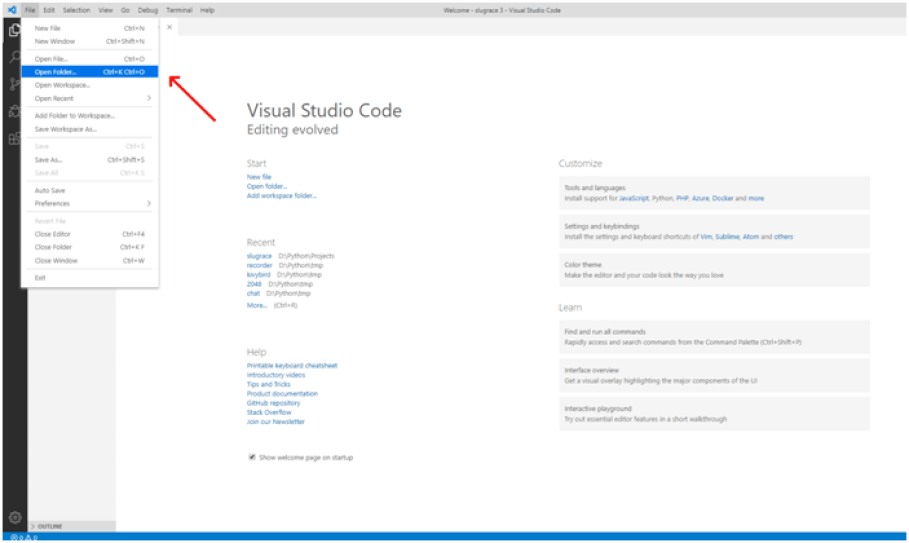
Open folder in VSC
Create a new virtual environment for your Kivy project. A virtual environment will prevent possible installation conflicts with other Python versions and packages. It’s optional but strongly recommended, open a New Terminal window and run the following:
- Open a Terminal window and create the virtual environment named .env in your current directory:
python -m venv .venv - Update the security on this folder
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process - Activate your new virtual environment.
.venv\scripts\activate - Install Kivy
python -m pip install kivy
If you get SSL errors use the following to install Kivy etc
pip3 install --trusted-host pypi.org --trusted-host files.pythonhosted.org kivyWhen you open your folder, you need a file to write the code to. This is going to be a regular Python file, so with the extension .py. You can name your file whatever you like, I’ll name mine main.py. Here’s how you can create the file: When you hover your mouse over the name of your folder, a menu with a couple icons will appear. The first icon is the one you should click to create a new file:
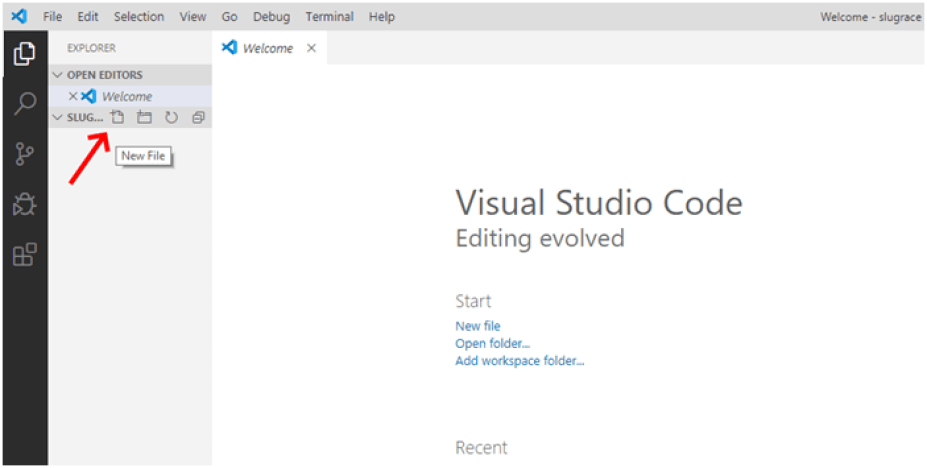
Open folder in VSC
All you have to do is type in the name of the file: main.py. As soon as you confirm by hitting Enter, the new file will be listed in the folder (A) and it will open automatically in a new tab (B). This is how we are going to add new files in the future.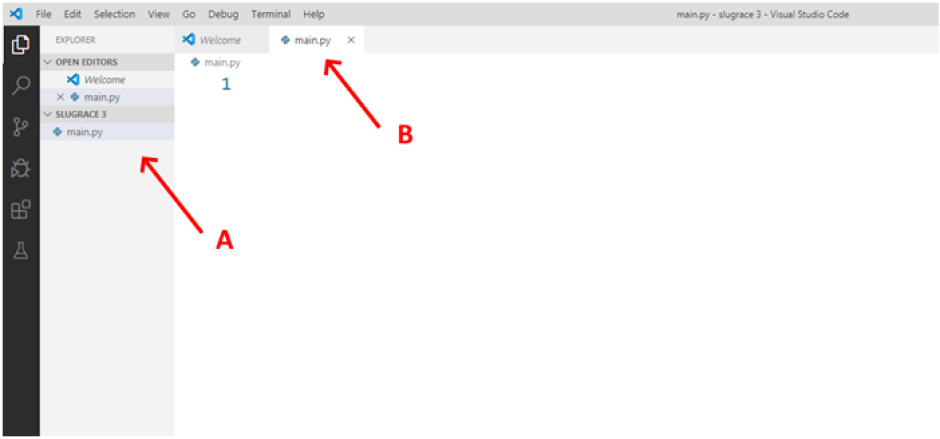
Open folder in VSC
Now we are ready to write our code. Here it is with comments:
| |
This is a basic Kivy application. Now we are ready to run it. There are several ways you can do it. Let’s have a look at the most obvious ones:
The first way to run the app is by pressing the Run Python File in Terminal button in the upper right corner (A). Here’s what we get when we do that: the application window shows up with our application running in it (B) and the terminal opens at the bottom with the Kivy log (C).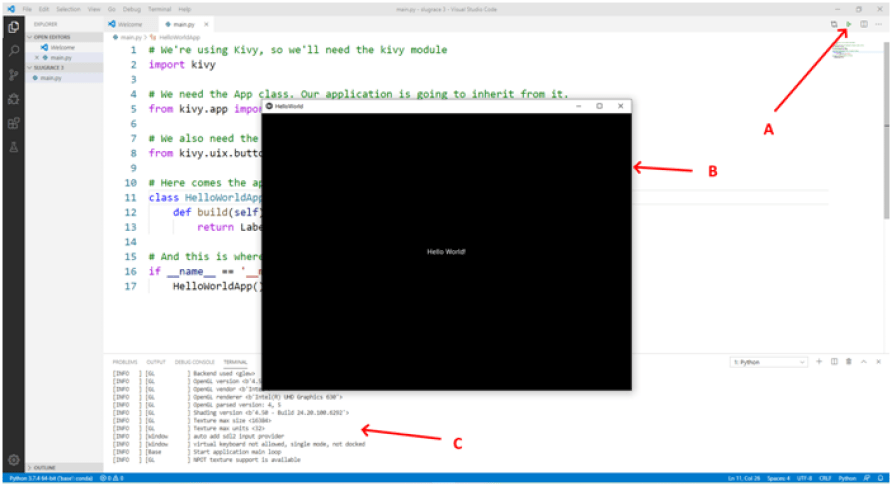
Run Python File in Terminal button
You can also go to the Debug menu and select Run Without Debugging: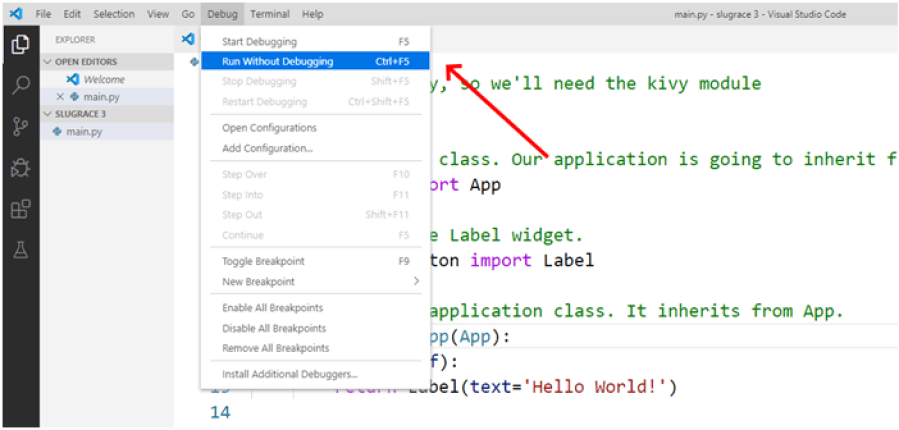
Run the Kivy App Without Debugging
There is also the Start Debugging option in the Debug menu. You can choose it and then select a Debug Configuration. Go ahead and select the first option, Python File: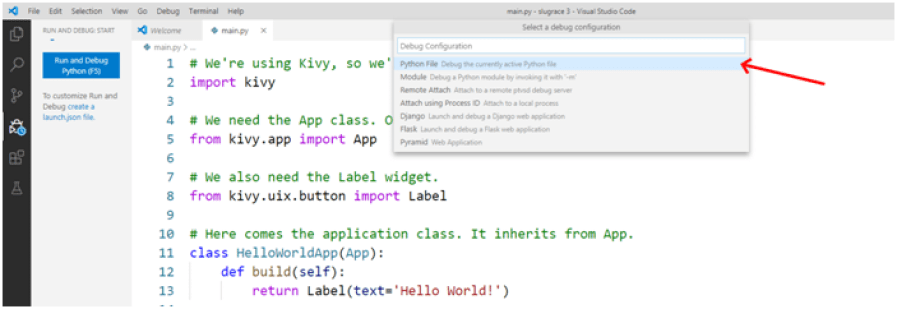
Start Debugging option in the Debug menu
For the previous two options you can also use hotkeys:
– F5 to start debugging
– Ctrl + F5 to run without debugging
You can also right-click anywhere in the editor tab where the code of your file is and select Run Python File in Terminal: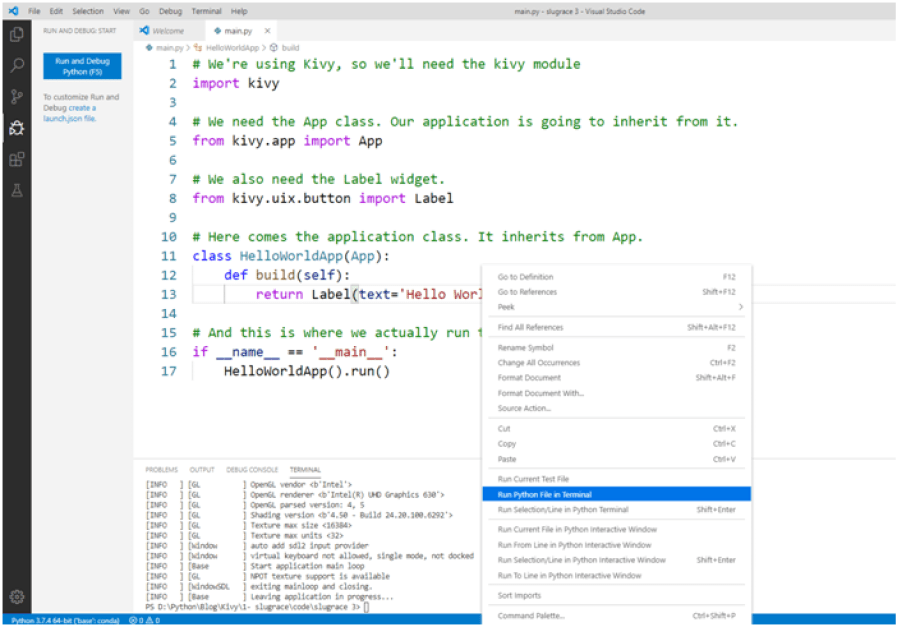
Context menu